For years, I eagerly anticipated Apple’s fall event and news of the latest iPhone release. Back then, my purchasing latency was limited to locating the website’s “buy” button, as my incumbent phone was often struggling to keep pace with new apps and software updates. Then, starting around 2015 (the iPhone 6S), I was able to start squeezing extra years out of my phones. This trend accelerated, and as of today, I still rely on my iPhone 11 Pro from 2019. To be fair, I always buy the top-end model with maximum storage, but four and a half years on, I haven’t crashed (at least not hard) into this phone’s silicone ceiling.
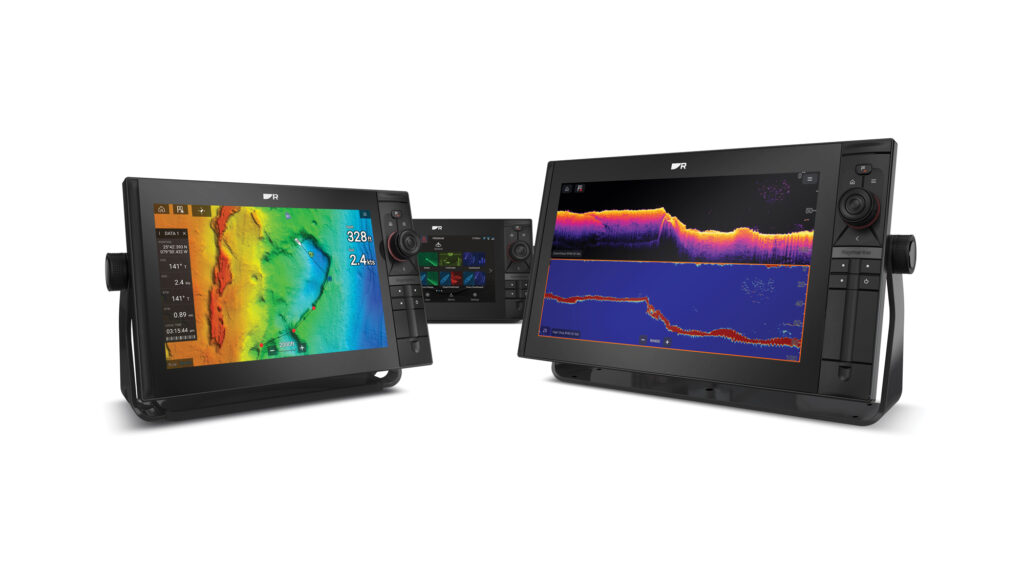
Multifunction displays perform different tasks than smartphones, but most marine-electronics manufacturers build MFDs with off-the-shelf componentry and, sometimes, software from the mobile-device market. This sourcing gives manufacturers options for high-resolution touchscreen displays, processors, connectivity and operating-system architecture, and it means that today’s MFDs can have longer working lives.
How we got here, however, requires a small rewind. After all, MFDs circa 2010 were different animals than today’s big, powerful displays.
“Back then, most displays were 4 to 7 inches,” says Dave Dunn, Garmin’s senior director of marine and RV sales. “A big display was 9 to 10 inches, and a 12-inch display was enormous.”
These MFDs were controlled via tactile buttons and knobs, or early touchscreen or hybrid-touch interfaces. They only tackled marine-facing applications such as chart-plotting.
Today’s MFDs excel at traditional marine tasks, but they also boast bigger glass, full video integration, touchscreen interfaces, high-speed data networks, and four- or six-core processors, opening the door to expanded job descriptions.
“Processing power has indeed increased over time, bringing with it the ability to drive higher-resolution screens,” says Steve Thomas, Simrad’s product director for digital systems. “[This] also lends itself to better integration by providing the responsiveness consumers expect.”
It also enables MFDs to perform nontraditional tasks, including streaming video from daylight and thermal-imaging cameras, tackling onboard security, controlling digital switching and, sometimes, providing entertainment. Today’s flagship MFDs also sport larger high-resolution displays, multisignal connectivity (with ANT, Bluetooth, Ethernet and Wi-Fi), embedded sonar modules, GPS or GNSS receivers, data backbones, and NMEA 2000 and HTML5 compatibility.
“NMEA 2000 protocol provides the basis of communication and is the linchpin connecting everything together for the MFD to display and control,” says Eric Kunz, Furuno’s senior product manager. Kunz adds that HTML5 compatibility allows MFDs to display and control third-party equipment via web-browser windows, sans any heavy lifting from the MFD.
Technology moves in step changes, and MFDs, brand depending, have experienced two major evolutions since 2010.
“The first was the transition from a completely closed-software architecture to something open source,” says Jim McGowan, Raymarine’s Americas marketing manager, referring to the company’s shift from a walled-garden operating system to Linux and then Android.
Others, including Simrad and Furuno, took similar steps. Garmin remains a holdout.
“We use Android, but not for marine,” Dunn says. “Will we eventually go to Android? Maybe.”
The second evolution involved hardware, with all MFD manufacturers now using mobile-device componentry.
“Suddenly, the requirements for shock resistance, heat resistance, water resistance, bright visibility and fast processing became available on a wide scale,” McGowan says. “Instead of us having to source expensive industrial or semicustom hardware that was proven but old, suddenly our system architects had multiple options to choose from that were all state of the art.”
Sourcing components became easier, yielding better MFDs, but it placed a higher premium on software. Case in point: Raymarine has released more than 30 updates, including new features, for its 2017-era Axiom MFDs.
Likewise, there’s the importance of supporting hardware as it ages. “We don’t like to leave customers behind,” Dunn says, noting that Garmin supports products for five years after they’re discontinued.
This opens the door to the fine art of good enough. Given that modern MFDs are robust, the same display—like my iPhone—can last for years, provided that its sensor network remains static. While this works for buy-and-hold customers, new sensors can dangle carrots.
For example, Furuno and Garmin unveiled Doppler-enabled radars in 2016. While older MFDs could often display radar imagery from these sensors, some customers had to refit their displays to access the best features. One can imagine automation and AI presenting similar incentives.
“AI will combine multiple facets of different sensors to create a more sophisticated and enhanced navigation experience,” Kunz says. “Look for MFDs to take a larger and larger part in overall vessel control and automation.”
Avikus, for instance, is developing its NeuBoat autonomous navigation system with Raymarine. As for Garmin, Dunn says: “There’s nothing coming in the near future, but there’s some cool stuff coming with lidar and cameras.” He’s referring to the light-detection and ranging sensors that help enable automotive driver-assist features and autonomous driving.
Future hardware and capabilities aside, all experts agree on the importance of regularly updating a vessel’s MFD to keep the operating system current and to access the latest software features. While updates are free, all four companies have adopted subscription models for cartography.
“In some ways, the marine-electronics business model is changing in the same way it is happening in the consumer-electronics industry,” Kunz says. “This will most likely lead to more of a subscription-based model for certain aspects of the market.”
While subscription models make sense for a dynamic media like cartography, it’s harder to envision this business practice extending throughout the sensor ecosystem.
“We don’t want to get to the point where people have to pay for software updates,” Dunn says, pointing to BMW’s belly-flopped attempt to charge customers fees to use their existing heated steering wheels.
New hardware, however, is a different story. “More than anything, we’re a sensor company,” McGowan says of Raymarine. “We keep offering new and improved sensors.”
Given the adoption rates of Doppler-enabled radar, there’s little question that the recreational marine market stands ready to embrace step-change sensors, so long as they come bundled with newfound capabilities—say, auto-docking or autonomous navigation.
As for my ancient iPhone, I’m again counting the days until Apple’s fall event. I just hope my next iPhone will last as long as today’s flagship MFDs.
UI Options
Recent years have seen most manufacturers adopt touchscreen-only user interfaces for their flagship multifunction displays. This technology creates user-friendly interfaces in most conditions, but some users prefer tactile buttons when the weather sours. All manufacturers build optional external keypads or hard-button remote controls.









